Solution Architecture: Designing the Platforms of Tomorrow
Table of Contents
Solution Architecture - This article is part of a series.
What is Solution Architecture? #
Solution architecture is a critical aspect of designing and building complex software systems that meet the needs of modern organizations. With the rise of cloud computing and containerization technologies like OpenShift and Kubernetes, solution architecture has become more important than ever, as organizations seek to build scalable, resilient, and flexible systems that can adapt to changing business needs.
In this blog series, we’ll explore the fundamentals of solution architecture and how they apply to OpenShift and Kubernetes-based systems.
In the next post, we’ll discuss the key principles of solution architecture, including scalability, availability, security, and performance, and how they can be achieved using OpenShift and Kubernetes.
In the final part of the series, we’ll look at some real-world examples of solution architecture in action, and provide practical tips and best practices for designing and implementing effective solutions using these technologies.
Whether you’re new to solution architecture or an experienced practitioner, this post will hopefully provide valuable insights and guidance for building better software systems on OpenShift and Kubernetes.
Taxonomy of a Solution #
Let’s say you have a customer that needs to modernize their legacy workloads and development environments, for one reason or another. Regardless of whether that determination has already been made, or they have approached you with a problem statement that leads towards that solution. How do you proceed from the client’s problem state to the reference implementation? And then how do you convert that into a reference architecture, and finally your final Solution?
The Solution Lifecycle #
The questions being asked above represent a customer Journey, or Transformation Journey. This is a big-picture objective and is the focus of the eventual solution which will be proposed and implemented.
A Journey will consist of 1 or more Architecture Patterns, each of which enable the vision of the Journey.
Each Architecture Pattern generally consists of Implementation Patterns based on prior work. Of course, cutting-edge technologies may not have prior-work to base the patterns on, but there is generally some form of similar implementation.
Architecture Decisions (ADs) provide detailed overviews of various technologies which address a specific, common decision point in designing a solution.
Reference Implementations are similar to Implementation Patterns, but specific to distinct technologies. They provide accelerators for these technologies to enable their use in larger solutions. In some cases, this may be the smallest component in the Solution Lifecycle.
Reference vs Solution #
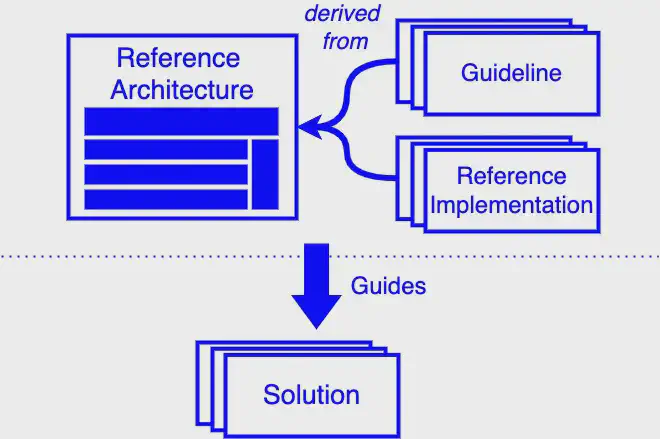
As you can see in the above image, Solution Architectures are guided by decisions made in Reference Architectures. But it does not show the rest of the cycle, where experiences from the solution redefine the underlying references.
Journeys #
A path forward representing the transformation of a particular objective.
Transformation Themes #
Per the Patterns Drive Playbook:
Transformation themes enable logical grouping of the various transformation patterns, and align with the Experiential Architecture Journey approach.
The 5 Transformation Themes:
- Innovate - New genre of applications developed on hybrid cloud/container platform
- Modernize - Related to application modernization scenarios
- Integrate - Integration scenarios with cloud / non cloud world to create a holistic hybrid cloud
- Optimize - Infra / App move scenarios with no functional change to apps
- Manage - Deploy, manage and operate across hybrid and edge environments
Patterns #
Patterns make up a considerable portion of solution architectures, especially within architecture-driven companies like IBM. Patterns are a repeatable set of items that lay groundwork for future work. These help to define best practices and enable future generations of architects to learn from prior work.
There are several important groups of Patterns within the domain of Solution Architecture. 2 overarching buckets are:
- Architecture Patterns
- Implementation Patterns
Architecture Patterns #
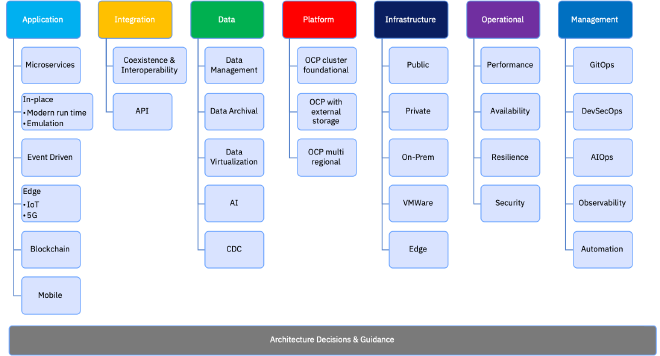
Architecture Patterns are a large grouping of patterns focused around solutioning new architectures. These include the following:
- Application
- Data
- Integration
- Platform
- Infra
- Operational
- Management
Implementation Patterns #
Implementation Patterns are a grouping of patterns focused around the implementation of technologies, frameworks, etc based upon prior work. These Patterns consist of a collection of Architecture Patterns and their related solutions to solve specific problems.
Reference Implementations #
An example of an implementation to drive solutions for a Journey, as well as to reference back to for future work.
