AWS Lambda vs OpenShift Serverless: A Detailed Comparison
Table of Contents
Serverless Servers - This article is part of a series.
Introduction #
Welcome back to MeatyBytes.io! Today, we’re going to diverge a bit from the dive down Knative and OpenShift Serverless to do a brief comparison with another powerful serverless platform: AWS Lambda. Both platforms offer robust features for deploying and managing serverless applications, but they each have their own strengths and use cases.
In this post, we’ll provide examples on how AWS Lambda can be integrated into an OpenShift cluster and why it might be used. We’ll also explore how it can be used to help manage an OpenShift cluster hosted on AWS. Finally, we’ll discuss why you might choose one platform over the other in various scenarios.
Let’s get started!
AWS Lambda vs OpenShift Serverless: An Overview #
Before we dive into the details, let’s briefly review what AWS Lambda and OpenShift Serverless are.
AWS Lambda is a serverless computing service provided by Amazon Web Services. It allows you to run your code without provisioning or managing servers. AWS Lambda automatically scales your applications in response to incoming requests, and you only pay for the compute time you consume.
OpenShift Serverless, powered by Knative, is a fully integrated part of the OpenShift ecosystem. It leverages the power of Kubernetes and the simplicity of Knative to provide a seamless serverless experience. OpenShift Serverless automatically scales your applications based on demand, and it can run on any Kubernetes cluster, providing more flexibility.
Integrating AWS Lambda into an OpenShift Cluster #
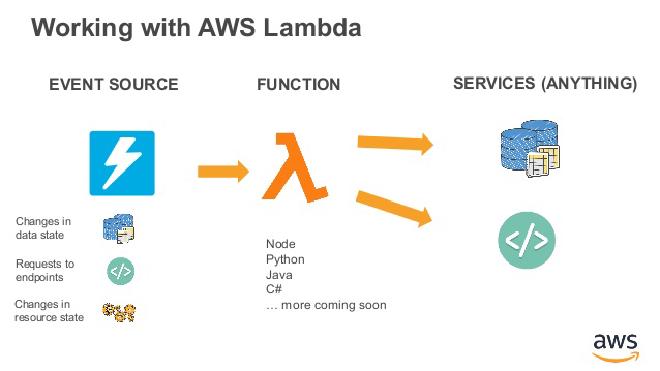
While AWS Lambda and OpenShift Serverless are separate platforms, they can be used together in a hybrid cloud setup. For example, you might have an OpenShift cluster hosted on AWS, and you want to use AWS Lambda to handle certain tasks.
Here’s a basic example of how you might integrate AWS Lambda into an OpenShift cluster:
- Create an AWS Lambda function: First, you’ll need to create a Lambda function in the AWS Management Console. This function will contain the code that you want to run in response to certain events.
- Create an OpenShift Route: Next, you’ll need to create a Route in OpenShift that points to your Lambda function. This Route will provide a URL that can be used to trigger your Lambda function.
- Trigger the Lambda function: Finally, you can trigger your Lambda function by sending a request to the Route’s URL. This could be done manually, or it could be automated using OpenShift’s built-in cron jobs or event triggers.
Using AWS Lambda to Manage an OpenShift Cluster on AWS #
AWS Lambda can also be used to help manage an OpenShift cluster hosted on AWS. For example, you might use Lambda functions to automate routine tasks, such as scaling your cluster, backing up data, or monitoring performance.
Here’s a basic example of how you might use AWS Lambda to scale your OpenShift cluster:
- Create an AWS Lambda function: This function will contain the code to scale your OpenShift cluster. This might involve making API calls to the AWS Auto Scaling service.
- Create a CloudWatch alarm: Next, you’ll need to create a CloudWatch alarm that triggers your Lambda function when certain conditions are met. For example, you might trigger the function when CPU utilization exceeds a certain threshold.
- Scale your cluster: When the CloudWatch alarm is triggered, your Lambda function will run and scale your OpenShift cluster accordingly.
Choosing Between AWS Lambda and OpenShift Serverless #
Choosing between AWS Lambda and OpenShift Serverless depends on your specific needs and
circumstances. Here are a few scenarios where you might prefer one over the other:
- If you’re already using AWS services: AWS Lambda integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, such as S3, DynamoDB, and CloudWatch. If you’re already using AWS for your infrastructure, it might make sense to use AWS Lambda for your serverless applications.
- If you want more flexibility: OpenShift Serverless can run on any Kubernetes cluster, not just those hosted on AWS. This gives you more flexibility to choose where to host your applications. If you’re using a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud setup, or if you’re hosting your cluster on-premises, OpenShift Serverless might be a better fit.
- If you’re using OpenShift: OpenShift Serverless is fully integrated with the OpenShift ecosystem, including its developer console, CLI, and APIs. If you’re already using OpenShift, it might be easier and more convenient to use OpenShift Serverless for your serverless applications.
Conclusion #
Both AWS Lambda and OpenShift Serverless are powerful platforms for deploying and managing serverless applications. While AWS Lambda offers tight integration with other AWS services, OpenShift Serverless provides more flexibility and a seamless experience for OpenShift users. By understanding the strengths and use cases of each platform, you can make an informed decision about which one is right for your needs.
As always, if you have any questions or run into any issues, don’t hesitate to reach out. Happy coding!
References #
For additional reading, check out the following resources:
- AWS Lambda Documentation
- OpenShift Serverless Documentation
- Why and When you need to consider OpenShift Serverless
- AWS Auto Scaling Documentation
- Amazon CloudWatch Documentation
